Cost Depletion: Meaning, Formula, Example
Then, multiply this figure by the number of units of goods or services produced during the accounting period to find the period’s depreciation expense. The percentage depletion method gives a fixed percentage of the gross income obtained from a natural resource. If a company has $5 million in gross income from a resource and wants to use a 15% depletion rate over a given period, its depletion deduction would amount to $750,000 million. Cost depletion is calculated by taking the property’s basis, total recoverable reserves and number of units sold into account.
Cost depletion
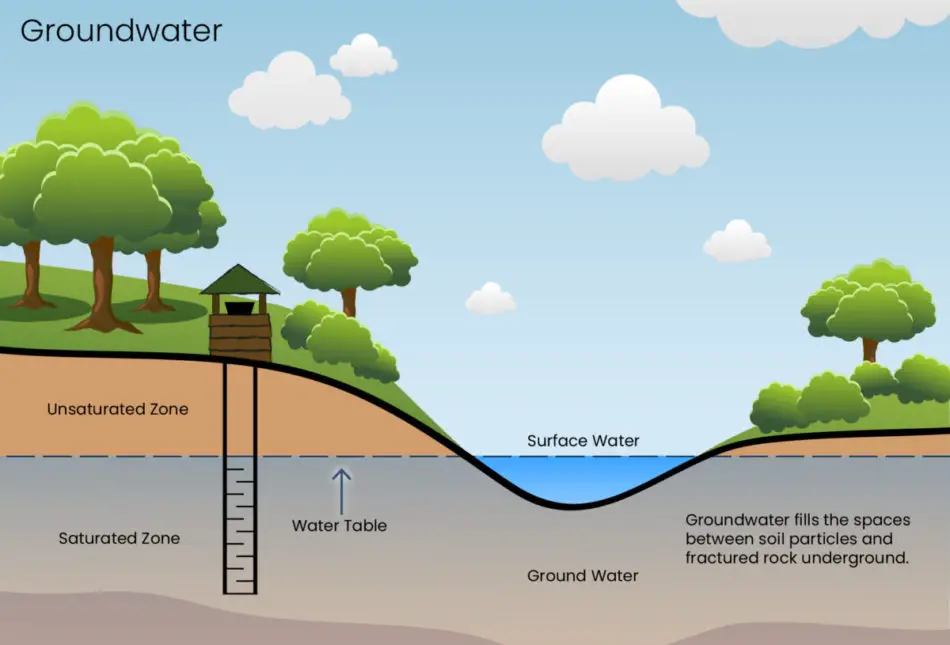
Depletion can only be used for natural resources, while depreciation is allowed for all tangible assets. Unlike depreciation, cost depletion is based on usage and must be calculated every period. Because the percentage depletion looks at the property’s gross income and taxable income limit, as opposed to the amount of the natural resource extracted, it is not an acceptable reporting method for certain natural resources. Depletion method of depreciation is mostly used by the companies that have assets that are natural resources like oil, gas, coal, mines, quarries or other wasting assets. Depletion is the process by which natural resources lose their benefits as the resources are removed. It follows the same process used in the units of production method of depreciation.
Our Team Will Connect You With a Vetted, Trusted Professional
At the point where book value is equal to the salvage value, no more depreciation is taken. The tax implications of depletion depend on the country in which the natural resources are located. In some countries, depletion is treated as a deductible expense for tax purposes. In addition, Pensive Oil estimates it will incur a site restoration cost of $57,000 once extraction is complete, making the total depletion base of the property $600,000. In addition, Pensive Oil estimates that it will incur a site restoration cost of $57,000 once extraction is complete, so the total depletion base of the property is $600,000.
- In some countries, depletion is treated as a deductible expense for tax purposes.
- Pensive’s geologists estimate the proven oil reserves accessed by the well are 400,000 barrels, so the unit depletion charge will be $1.50 per barrel of oil extracted ($600,000 depletion base / 400,000 barrels).
- The depletion rate per unit of a natural resource or asset depends upon the total number of units expected to be extracted.
- Such assets are also referred as wasting assets because their value deteriorates with the increasing extraction of resources.
- We follow strict ethical journalism practices, which includes presenting unbiased information and citing reliable, attributed resources.
- The property’s basis is distributed among the total number of recoverable units.
Example of How to Use Cost Depletion

But unless you’re an independent producer or royalty owner, the IRS says you usually can’t use the percentage depletion method for oil and gas wells. The resulting net carrying amount of natural resources still on the books of a business do not necessarily reflect the market value what is the liability to equity ratio of chester of the underlying natural resources. The depletion base comprises of cost incurred to acquire or lease the asset, exploration cost, development cost and any cost incurred to restore the property to its original condition after the assets or resources have been fully depleted.
Why You Can Trust Finance Strategists
In the first year, Pensive Oil extracts 100,000 barrels of oil from the well, which results in a depletion charge of $150,000 (100,000 barrels x $1.50 unit depletion charge). Depletion is an accrual accounting technique used to allocate the cost of extracting natural resources such as timber, minerals, and oil from the earth. Depletion is the reduction in the amount of a natural resource, such as minerals or timber. From an accounting perspective, it is a charge against the recorded asset value of a natural resource. This charge is made in each reporting period, in an amount that reflects the level of asset usage during the period. Depletion for accounting and financial reporting purposes is meant to assist in accurately identifying the value of the assets on the balance sheet and recording expenses in the appropriate time period on the income statement.
AccountingTools
Cost depletion is calculated by estimating the total quantity of a given resource and then dividing the percentage withdrawn by the total quantity. Let’s say an oil company expects to spend $200,000 to withdraw 50,000 barrels of oil every year from a field with estimated reserves of 1 million barrels. The amount of depletion that could be claimed would be $10,000, or $200,000(50,000/1,000,000). At the start of the year 2, a new survey is conducted and it is found that the expected extraction of minerals is only 160,000 tons (i.e.,40,000 tons less then the original estimate). The company decided to workout a new depletion rate on the basis of information provided by revised survey.
The depletion rate per unit of a natural resource or asset depends upon the total number of units expected to be extracted. This is calculated by dividing the depletion base less salvage value (if any) by the number of units expected to be extracted. Since the amount of depreciation may be relatively large, depreciation expense is often a significant factor in determining net income. For this reason, most financial statement users are interested in the amount of, and the methods used to compute, a company’s depreciation expense.
For example in case of a coal mine, more the coal is extracted more will be the depletion of the mine etc. Useful life refers to the time the company owning the asset intends to use it; useful life is not necessarily the same as either economic life or physical life. The economic life of a car may be 7 years and its physical life may be 10 years, but if a company has a policy of trading cars every 3 years, the useful life for depreciation purposes is 3 years. Various firms express useful life in years, months, working hours, or units of production.
- Trending
- Latest

Common Biology Preparation Problems Solved – Pathfinder Institute Apr 09 2024

Common Chemistry Preparation Problems Solved – Pathfinder Institute Apr 08 2024

Common Mathematics Problems Solved – Pathfinder Institute Apr 06 2024

Common Physics Problems Solved – Pathfinder Institute Apr 02 2024

JEE 2024 Counselling Process – Pathfinder Institute Feb 08 2024

NEET 2024 Counselling Process – Pathfinder Institute Feb 08 2024

Best Medical Colleges in India for NEET 2024 Aspirants – Pathfinder Institute Feb 02 2024

Best IITs and NITs In India – Pathfinder Institute Feb 01 2024

Madhyamik 2024 Last Minute Preparation – Pathfinder Institute Jan 20 2024

ICSE 2024 Exam Date Out! Pathfinder Institute Dec 08 2023
Сколько игровых автоматов есть у онлайн казино Up X? Dec 21 2024
Install PinUp app 💰 Free spins for beginners 💰 Play Online Casino Games Dec 21 2024
Taglist
- WBJEE 2025 Repeaters
- NEET 2025 Repeaters
- JEE Main 2025 Repeaters
- JEE Advanced 2025 Repeaters
- SOF
- Olympiads
- SOF IMO & NSO 2024 Exam Schedule
- WBJEE 2024 Preparation Stress
- NEET 2024 Correction Window
- H.S 2025 Board Exam
- H.S 2025 Examination
- H.S 2025 Exam
- H.S 2025 Science Preparation
- H.S 2025 Science Suggestion
- H.S 2025 Science
- H.S 2025 Preparation
- H.S 2025 Suggestions
- H.S 2025
- H.S. 2025 Board Exam
- H.S. 2025 Official Notice
- H.S. 2025 Exam Pattern
- H.S. 2025 Instructions
- H.S. 2025 Result
- H.S. 2025 Syllabus
- H.S. 2025 Exam Date
- h.s. 2025 routine
- Biology Problems Solved
- Common Biology Class 10 Problems
- Biology Class 12 Problems
- Biology Chemistry Problems
- Biology Chemistry Problems Solved
- Common Biology Problems Solutions
- Chemistry Problems Solved
- Common Chemistry Class 10 Problems
- Chemistry Class 12 Problems
- Common Chemistry Problems
- Common Chemistry Problems Solved
- Common Chemistry Problems Solutions
- Mathematics Problems Solved
- Common Mathematics Class 10 Problems
- Mathematics Class 12 Problems
- Common Mathematics Problems
- Common Mathematics Problems Solved
- Common Mathematics Problems Solutions
- Counselling Process for WBJEE 2024
- WBJEE Counselling 2024
- WBJEE 2024 Counselling fees
- WBJEE 2024 Counselling Process
- wbjee 2024 counselling
- JEE Main 2024 Session 2
- Physics Problems Solved
- Physics Class 12 Problems
- Common Physics Class 10 Problems
- Common Physics Problems
- Common Physics Problems Solved
- JEE Advanced 2024 motivation
- WBJEE 2024 Motivation
- NEET 2024 Motivation
- WBJEE 2024 Top Mistakes
- JEE Advanced 2024 Top Mistakes
- NEET 2024 Top Mistakes
- Math Madhyamik 2025
- Life Science Madhyamik 2025
- Lif Science Madhyamik 2025
- Madhyamik 2025 Board Exam
- Madhyamik 2025 examination
- Madhyamik 2025 exam
- Madhyamik 2025 science preparation
- Madhyamik 2025 science suggestion
- Madhyamik 2025 science
- Madhyamik 2025 preparation
- Madhyamik 2025 suggestions
- Madhyamik 2025
- Physical Science Madhyamik 2025
- NEET 2024 registration
- INMO
- RMO
- Indian National Mathematical Olympiad
- Regional Mathematical Olympiad
- Third stage exam: Indian National Mathematical Olympiad (INMO)
- IOQM 2024
- VSO 2024 Examination
- Vidyasagar Science Olympiad 2024
- VSO 2024 Result
- VSO result layer 3
- VSO result layer 2
- VSO 2024
- JEE Advanced Mathematics Important Topics 2024
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Important Topics 2024
- JEE Advanced Physics Important Topics 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024 Strategy
- JEE Advanced 2024 Last-Minute Preparation Strategy
- JEE Advanced Preparation Strategy
- NEET 2024 Strategy
- NEET 2024 Preparation
- NEET 2024 Preparation Strategy
- WBJEE 2024 Chemistry Tips
- WBJEE 2024 Preparation
- WBJEE 2024 Chemistry
- WBJEE 2024 Preparation Chemistry
- WBJEE 2024 Physics Tips
- WBJEE Mathematics
- WBJEE 2024 Mathematics
- WBJEE 2024 Preparation Tips
- WBJEE Coaching In Arambagh
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Arambagh
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Aramba
- Top WBJEE Coaching In Arambagh
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Arambagh
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Arambagh
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Arambagh
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Arambagh
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Arambagh
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In Arambagh
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In Arambagh
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In Arambagh
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In Arambagh
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In Arambagh
- ICSE Mathematics
- ICSE Math 2024
- ICSE MATHS
- ICSE Biology
- icse civics
- icse geography
- icse history
- ICSE Physics
- ICSE Chemistry
- istry
- ICSE Che
- ICSE 2024 Chemistry
- ICSE 2024 Physics
- ICSE 2024 English
- ICSE English
- JEE 2024 Counselling Process In India
- JEE 2024 Counselling Process
- JEE Counselling Process
- Engineering Colleges In Kolkata
- Best Engineering Colleges In West BengalBest Engineering Colleges In West Bengal
- Best Engineering Colleges
- Top 10 Engineering Colleges
- JEE 2024 Colleges
- JEE 2024 College In India
- JEE Medical Colleges
- JEE College
- JEE Colleges
- neet 2024 counselling process in India
- neet 2024 counselling process
- neet counselling process
- medical colleges in Kolkata
- best medical colleges in west bengal
- best medical colleges
- top 10 medical colleges
- NEET 2024 College in India
- NEET 2024 Colleges
- NEET Medical colleges
- NEET college
- NEET Colleges
- NEET 2024 Colleges]
- NITS
- IIITS
- INDIA
- iits
- Top JEE Coaching In West Bengal
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In West Bengal
- JEE Coaching Centre In West Bengal
- Best JEE Coaching Institute In West Bengal
- JEE Coaching Institute In West Bengal
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In West Bengal
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In West Bengal
- Coaching Centre For JEE In West Bengal
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In West Bengal
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In West Bengal
- Best JEE Coaching In West Bengal
- Coaching Institute For JEE In West Bengal
- Best WBJEE Coaching In West Bengal
- Top WBJEE Coaching In West Bengal
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In West Bengal
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In West Bengal
- Best WBJEE Coaching Institute In West Bengal
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In West Bengal
- Top Coaching Centre For WBJEE In West Bengal
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In West Bengal
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In West Bengal
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In West Bengal
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In West Bengal
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In West Bengal
- Coaching Institute For NEET In West Bengal
- Best Coaching Institute For NEET In West Bengal
- Top Coaching Institute For NEET In West Bengal
- Coaching Centre For NEET In West Bengal
- Best Coaching Centre For NEET In West Bengal
- Top Coaching Centre For NEET In West Bengal
- NEET Coaching Institute In West Bengal
- Best NEET Coaching Institute In West Bengal
- NEET Coaching Centre In West Bengal
- Best NEET Coaching Centre In West Bengal
- Top NEET Coaching In West Bengal
- Best NEET Coaching In West Bengal
- JEE Main 2024 last minute tips
- JEE Main 2024 last minute suggestions
- JEE Main 2024 last minute suggestion
- #madhyamik madhyamik
- #madhyamik
- Top NEET Coaching Centre In Kishanganj Bihar
- Best NEET Coaching Centre In Kishanganj Bihar]
- NEET Coaching Centre In Kishanganj Bihar
- Top NEET Coaching Institute In Kishanganj Bihar
- NEET Coaching Institute In Kishanganj Bihar
- Best Coaching Centre For NEET In Kishanganj Bihar
- Coaching Centre For NEET In Kishanganj Bihar
- Top Coaching Institute For NEET In Kishanganj Bihar
- Coaching Institute For NEET In Kishanganj Bihar
- Best Coaching Institute For NEET In Kishanganj Bihar
- Top NEET Coaching In Kishanganj Bihar
- NEET Coaching In Kishanganj Bihar
- Best NEET Coaching In Kishanganj Bihar
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Kishanganj Bihar
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Kishanganj Bihar
- JEE Coaching Centre In Kishanganj Bihar
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Kishanganj Bihar
- JEE Coaching Institute In Kishanganj Bihar
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Kishanganj Bihar
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Kishanganj Bihar
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Kishanganj Bihar
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Kishanganj Bihar
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Kishanganj Bihar
- Top JEE Coaching In Kishanganj Bihar
- JEE Coaching In Kishanganj Bihar
- Best JEE Coaching In Kishanganj Bihar
- H.S. 2024 Time Table
- H.S. 2024 Board Exam
- H.S. 2024 Official Notice
- H.S. 2024 Exam Pattern
- H.S. 2024 Instructions
- H.S. 2024 Result
- H.S. 2024 Syllabus
- H.S. 2024 Exam Date
- Madhyamik 2024 Exam Date
- Madhyamik 2024 Syllabus
- Madhyamik 2024 Result
- Madhyamik 2024 Instructions
- Madhyamik 2024 Exam Pattern
- Madhyamik 2024 Exam Schedule
- Madhyamik 2024 Official Notice
- Madhyamik 2024 Board Exam
- Madhyamik 2024 Time Table
- JEE Coaching In Tarakeswar
- Best JEE Coaching In Tarakeswar
- Top JEE Coaching In Tarakeswar
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Tarakeswar
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Tarakeswar
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Tarakeswar
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Tarakeswar
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In Tarakeswar
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Tarakeswar
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Tarakeswar
- JEE Coaching Institute In Tarakeswar
- JEE Coaching Centre In Tarakeswar
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Tarakeswar
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Tarakeswar
- The Best JEE Coaching In Tarakeswar
- Best JEE Coaching In Tamluk
- JEE Coaching In Tamluk
- Top JEE Coaching In Tamluk]
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Tamluk
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Tamluk
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Tamluk
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Tamluk
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Tamluk
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Tamluk
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In Tamluk
- JEE Coaching Institute In Tamluk
- JEE Coaching Centre In Tamluk
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Tamluk
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Tamluk
- The Best JEE Coaching In Tamluk
- JEE Coaching In Siliguri
- Best JEE Coaching In Siliguri
- Top JEE Coaching In Siliguri
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Siliguri
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Siliguri
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Siliguri
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Siliguri
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Siliguri
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In Siliguri
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Siliguri
- JEE Coaching Institute In Siliguri
- JEE Coaching Centre In Siliguri
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Siliguri
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Siliguri
- The Best JEE Coaching In Siliguri
- JEE Coaching In Raiganj
- Best JEE Coaching In Raiganj
- Top JEE Coaching In Raiganj
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Raiganj
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Raiganj
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Raiganj
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Raiganj
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Raiganj
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Raiganj
- JEE Coaching Institute In Raiganj
- JEE Coaching Centre In Raiganj
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Raiganj
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Raiganj
- The Best JEE Coaching In Raiganj
- JEE Coaching In Midnapore
- Best JEE Coaching In Midnapore
- Top JEE Coaching In Midnapore
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Midnapore
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Midnapore
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Midnapore
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Midnapore
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Midnapore
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In Midnapore
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Midnapore
- JEE Coaching Institute In Midnapore
- JEE Coaching Centre In Midnapore
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Midnapore
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Midnapore
- The Best JEE Coaching In Midnapore
- JEE Coaching In KTPP
- Best JEE Coaching In KTPP
- Top JEE Coaching In KTPP
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In KTPP
- Coaching Institute For JEE In KTPP
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In KTPP
- Coaching Centre For JEE In KTPP
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In KTPP
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In KTPP
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In KTPP
- JEE Coaching Institute In KTPP
- JEE Coaching Centre In KTPP
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In KTPP
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In KTPP
- The Best JEE Coaching In KTPP
- JEE Coaching In Kharagpur
- Best JEE Coaching In Kharagpur
- Top JEE Coaching In Kharagpur
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Kharagpur
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Kharagpur
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Kharagpur
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Kharagpur
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Kharagpur
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In Kharagpur
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Kharagpur
- JEE Coaching Institute In Kharagpur
- JEE Coaching Centre In Kharagpur
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Kharagpur
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Kharagpur
- The Best JEE Coaching In Kharagpur
- JEE Coaching In Katwa
- Best JEE Coaching In Katwa
- Top JEE Coaching In Katwa
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Katwa
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Katwa
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Katwa
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Katwa
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Katwa
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In Katwa
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Katwa
- JEE Coaching Institute In Katwa
- JEE Coaching Centre In Katwa
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Katwa
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Katwa
- The Best JEE Coaching In Katwa
- JEE Coaching In Kalyani
- Best JEE Coaching In Kalyani
- Top JEE Coaching In Kalyani
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Kalyani
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Kalyani
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Kalyani
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Kalyani
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Kalyani
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In Kalyani
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Kalyani
- JEE Coaching Institute In Kalyani
- JEE Coaching Centre In Kalyani
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Kalyani
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Kalyani
- The Best JEE Coaching In Kalyani
- JEE Coaching In Howrah
- Best JEE Coaching In Howrah
- Top JEE Coaching In Howrah
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Howrah
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Howrah
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Howrah
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Howrah
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Howrah
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In Howrah
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Howrah
- JEE Coaching Institute In Howrah
- JEE Coaching Centre In Howrah
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Howrah
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Howrah
- The Best JEE Coaching In Howrah
- JEE Coaching In Habra
- Best JEE Coaching In Habra
- Top JEE Coaching In Habra
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Habra
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Habra
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Habra
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Habra
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Habra
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In Habra
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Habra
- JEE Coaching Institute In Habra
- JEE Coaching Centre In Habra
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Habra
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Habra
- The Best JEE Coaching In Habra
- JEE Coaching In Diamond Harbour
- Best JEE Coaching In Diamond Harbour
- Top JEE Coaching In Diamond Harbour
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Diamond Harbour
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Diamond Harbour
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Diamond Harbour
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Diamond Harbour
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Diamond Harbour
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In Diamond Harbour
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Diamond Harbour
- JEE Coaching Institute In Diamond Harbour
- JEE Coaching Centre In Diamond Harbour
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Diamond Harbour
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Diamond Harbour
- The Best JEE Coaching In Diamond Harbour
- JEE Coaching In Cooch Behar
- Best JEE Coaching In Cooch Behar
- Top JEE Coaching In Cooch Behar
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Cooch Behar
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Cooch Behar
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Cooch Behar
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Cooch Behar
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Cooch Behar
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In Cooch Behar
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Cooch Behar
- JEE Coaching Institute In Cooch Behar
- JEE Coaching Centre In Cooch Behar
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Cooch Behar
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Cooch Behar
- The Best JEE Coaching In Cooch Behar
- JEE Coaching In Contai
- Best JEE Coaching In Contai
- Top JEE Coaching In Contai
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Contai
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Contai
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Contai
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Contai
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Contai
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In Contai
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Contai
- JEE Coaching Institute In Contai
- JEE Coaching Centre In Contai
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Contai
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Contai
- The Best JEE Coaching In Contai
- JEE Coaching In Chandannagar
- Best JEE Coaching In Chandannagar
- Top JEE Coaching In Chandannagar
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Chandannagar
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Chandannagar
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Chandannagar
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Chandannagar
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Chandannagar
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In Chandannagar
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Chandannagar
- JEE Coaching Institute In Chandannagar
- JEE Coaching Centre In Chandannagar
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Chandannagar
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Chandannagar
- The Best JEE Coaching In Chandannagar
- JEE Coaching In Burdwan
- Best JEE Coaching In Burdwan
- Top JEE Coaching In Burdwan
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Burdwan
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Burdwan
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Burdwan
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Burdwan
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Burdwan
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In Burdwan
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Burdwan
- JEE Coaching Institute In Burdwan
- JEE Coaching Centre In Burdwan
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Burdwan
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Burdwan
- The Best JEE Coaching In Burdwan
- JEE Coaching In Bolpur
- Best JEE Coaching In Bolpur
- Top JEE Coaching In Bolpur
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Bolpur
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Bolpur
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Bolpur
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Bolpur
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Bolpur
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In Bolpur
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Bolpur
- JEE Coaching Institute In Bolpur
- JEE Coaching Centre In Bolpur
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Bolpur]
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Bolpur
- The Best JEE Coaching In Bolpur
- JEE Coaching In Berhampore
- Best JEE Coaching In Berhampore
- Top JEE Coaching In Berhampore
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Berhampore
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Berhampore
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Berhampore
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Berhampore
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Berhampore
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In Berhampore
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Berhampore
- JEE Coaching Institute In Berhampore
- JEE Coaching Centre In Berhampore
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Berhampore
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Berhampore
- The Best JEE Coaching In Berhampore
- JEE Coaching In Baruipur
- Best JEE Coaching In Baruipur
- Top JEE Coaching In Baruipur
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Baruipur
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Baruipur
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Baruipur
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Baruipur
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Baruipur
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In Baruipur
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Baruipur
- JEE Coaching Institute In Baruipur
- JEE Coaching Centre In Baruipur
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Baruipur
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Baruipur
- The Best JEE Coaching In Baruipur
- JEE Coaching In Barrackpore
- Best JEE Coaching In Barrackpore
- Top JEE Coaching In Barrackpore
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Barrackpore
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Barrackpore
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Barrackpore
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Barrackpore
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Barrackpore
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In Barrackpore
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Barrackpore
- JEE Coaching Institute In Barrackpore
- JEE Coaching Centre In Barrackpore
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Barrackpore
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Barrackpore
- The Best JEE Coaching In Barrackpore
- JEE Coaching In Barasat
- Best JEE Coaching In Barasat
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Barasat
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Barasat
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Barasat
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Barasat
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Barasat
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In Barasat
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Barasat
- JEE Coaching Institute In Barasat
- JEE Coaching Centre In Barasat
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Barasat
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Barasat
- The Best JEE Coaching In Barasat
- JEE Coaching In Bankura
- Best JEE Coaching In Bankura
- Top JEE Coaching In Bankura
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Bankura
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Bankura
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Bankura
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Bankura
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Bankura
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In Bankura
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Bankura
- JEE Coaching Institute In Bankura
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Bankura
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Bankura
- The Best JEE Coaching In Bankura
- JEE Coaching In Arambagh
- Top JEE Coaching In Arambagh
- Best JEE Coaching In Arambagh
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Arambagh
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Arambagh
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Arambagh
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Arambagh
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Arambagh
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In Arambagh
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Arambagh
- JEE Coaching Institute In Arambagh
- JEE Coaching Centre In Arambagh
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Arambagh
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Arambagh
- The Best JEE Coaching In Arambagh
- JEE Coaching In Agartala
- Best JEE Coaching In Agartala
- Top JEE Coaching In Agartala
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Agartala
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Agartala
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Agartala
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Agartala
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Agartala
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In Agartala
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Agartala
- JEE Coaching Institute In Agartala
- JEE Coaching Centre In Agartala
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Agartala]
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Agartala
- The Best JEE Coaching In Agartala
- ISC 2024 Result Date
- Pathfinder ISC 2024
- ISC 2024 Time Table
- ISC 2024 Board Exam
- ISC 2024 Official Notice
- ISC 2024 Exam Schedule
- ISC 2024 Exam Pattern
- ISC 2024 Instructions
- ISC 2024 Result
- ISC 2024 Syllabus
- ISC 2024 Exam Date
- Pathfinder ICSE 2024
- ICSE 2024 time table
- ICSE 2024 Board Exam
- ICSE 2024 Official Notice
- ICSE 2024 Exam Schedule
- ICSE 2024 Exam Pattern
- ICSE 2024 Instructions
- ICSE 2024 Result
- ICSE 2024 Syllabus
- ICSE 2024 Exam Date
- JEE Coaching In Balurghat
- Best JEE Coaching In Balurghat
- Top JEE Coaching In Balurghat
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Balurghat
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Balurghat
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Balurghat
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Balurghat
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Balurghat
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In Balurghat
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Balurghat
- JEE Coaching Institute In Balurghat
- JEE Coaching Centre In Balurghat
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Balurghat
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Balurghat
- The Best JEE Coaching In Balurghat
- JEE Coaching In Bally
- Best JEE Coaching In Bally
- Top JEE Coaching In Bally
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Bally
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Bally
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Bally
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Bally
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Bally
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In Bally
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Bally
- JEE Coaching Institute In Bally
- JEE Coaching Centre In Bally
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Bally
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Bally
- The Best JEE Coaching In Bally
- JEE Coaching In Bagnan
- Best JEE Coaching In Bagnan
- Top JEE Coaching In Bagnan
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Bagnan
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Bagnan
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Bagnan
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Bagnan
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Bagnan
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In Bagnan
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Bagnan
- JEE Coaching Institute In Bagnan
- JEE Coaching Centre In Bagnan
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Bagnan
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Bagnan
- The Best JEE Coaching In Bagnan
- JEE Coaching In Durgapur
- Best JEE Coaching In Durgapur
- Top JEE Coaching In Durgapur
- Best Coaching Institute For JEE In Durgapur
- Coaching Institute For JEE In Durgapur
- Top Coaching Institute For JEE In Durgapur
- Coaching Centre For JEE In Durgapur
- Best Coaching Centre For JEE In Durgapur
- Top Coaching Centre For JEE In Durgapur
- Top JEE Coaching Institute In Durgapur
- JEE Coaching Institute In Durgapur
- JEE Coaching Centre In Durgapur
- Best JEE Coaching Centre In Durgapur
- The Best JEE Coaching In Durgapur
- Top JEE Coaching Centre In Durgapur
- WBJEE Coaching In Tarakeswar
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Tarakeswar
- Top WBJEE Coaching In Tarakeswar
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Tarakeswar
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Tarakeswar
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Tarakeswar
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Tarakeswar
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Tarakeswar
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In Tarakeswar
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In Tarakeswar
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In Tarakeswar
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In Tarakeswar
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In Tarakeswar
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Kharagpur
- WBJEE Coaching In Kharagpur
- Top WBJEE Coaching In Kharagpur
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Kharagpur
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Kharagpur
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Kharagpur
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Kharagpur
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Kharagpur
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In Kharagpur
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In Kharagpur
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In Kharagpur
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In Kharagpur
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In Kharagpur
- WBJEE Coaching In Raiganj
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Raiganj
- Top WBJEE Coaching In Raiganj
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Raiganj
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Raiganj
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Raiganj
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Raiganj
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Raiganj
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In RaiganjWBJEE Coaching Institute In Raiganj
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In Raiganj
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In Raiganj
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In Raiganj
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In Raiganj
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In Raiganj
- WBJEE Coaching In KTPP
- Best WBJEE Coaching In KTPP
- Top WBJEE Coaching In KTPP
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In KTPP
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In KTPP
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In KTPP
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In KTPP
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In KTPP
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In KTPP
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In KTPP
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In KTPP
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In KTPP
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In KTPP
- WBJEE Coaching In Contai
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Contai
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Contai
- Top WBJEE Coaching In Contai
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Contai
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Contai
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Contai
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Contai
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In Contai
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In Contai
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In Contai
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In Contai
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In Contai
- WBJEE Coaching In Katwa
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Katwa
- Top WBJEE Coaching In Katwa
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Katwa
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Katwa
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Katwa
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Katwa
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Katwa
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In Katwa
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In Katwa
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In Katwa
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In Katwa
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In Katwa
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Durgapur
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Durgapur
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Durgapur
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Durgapur
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Durgapur
- Top Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Durgapur
- WBJEE Coaching In Diamond Harbour
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Diamond Harbour
- Top WBJEE Coaching In Diamond Harbour
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Diamond Harbour
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Diamond Harbour
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Diamond Harbour
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Diamond Harbour
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Diamond Harbour
- Top Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Diamond Harbour
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In Diamond Harbour
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In Diamond Harbour
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In Diamond Harbour
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In Diamond Harbour
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In Diamond Harbour
- WBJEE Coaching In Howrah
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Howrah
- Top WBJEE Coaching In Howrah
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Howrah
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Howrah
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Howrah
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Howrah
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Howrah
- Top Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Howrah
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In Howrah
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In Howrah
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In Howrah
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In Howrah
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In Howrah
- The best WBJEE Coaching in Howrah
- Top NEET Coaching Centre In Tarakeswar
- Best NEET Coaching Centre In Tarakeswar
- NEET Coaching Centre In Tarakeswar
- Best NEET Coaching Institute In Tarakeswar
- Best Coaching Centre For NEET In Tarakeswar Coaching Centre For NEET In Tarakeswar
- Top Coaching Centre For NEET In Tarakeswar
- NEET Coaching Institute In Tarakeswar
- Top Coaching Institute For NEET In Tarakeswar
- Best Coaching Institute For NEET In Tarakeswar
- Coaching Institute For NEET In Tarakeswar
- Top NEET Coaching In Tarakeswar
- Best NEET Coaching In Tarakeswar
- Top NEET Coaching Centre In Raiganj
- Best NEET Coaching Centre In Raiganj
- NEET Coaching Centre In Raigan
- Best NEET Coaching Institute In Raiganj
- NEET Coaching Institute In Raiganj
- Top Coaching Centre For NEET In Raiganj
- Best Coaching Centre For NEET In Raiganj
- Coaching Centre For NEET In Raiganj
- Top Coaching Institute For NEET In Raiganj
- Best Coaching Institute For NEET In Raiganj
- Coaching Institute For NEET In Raiganj
- Top NEET Coaching In Raiganj
- Best NEET Coaching In Raiganj
- Best NEET Coaching Centre In Katwa
- NEET Coaching Centre In Katwa
- Best NEET Coaching Institute In Katwa
- NEET Coaching Institute In Katwa
- Top Coaching Centre For NEET In Katwa
- Best Coaching Centre For NEET In Katwa
- Coaching Centre For NEET In Katwa
- Top Coaching Institute For NEET In Katwa
- Best Coaching Institute For NEET In Katwa
- Coaching Institute For NEET In Katwa
- Top NEET Coaching In Katwa
- Best NEET Coaching In Katwa
- NEET Coaching In Katwa
- Top NEET Coaching Centre In Habra
- Best NEET Coaching Centre In Habra
- NEET Coaching Centre In Habra
- Best NEET Coaching Institute In Habra
- NEET Coaching Institute In Habra
- Top Coaching Centre For NEET In Habra
- Best Coaching Centre For NEET In Habra
- Coaching Centre For NEET In Habra
- Top Coaching Institute For NEET In Habra
- Best Coaching Institute For NEET In Habra
- Coaching Institute For NEET In Habra
- Top NEET Coaching In Habra
- Best NEET Coaching In Habra
- NEET Coaching In Habra
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Habra
- WBJEE Coaching In Habra
- Top WBJEE Coaching In Habra
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Habra
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Habra
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Habra
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Habra
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Habra
- Top Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Habra
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In Habra
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In Habra
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In Habra
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In Habra
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In Habra
- Top NEET Coaching Centre In Contai
- Best NEET Coaching Centre In Contai
- NEET Coaching Centre In Contai
- Top NEET Coaching Institute In Contai
- Best NEET Coaching Institute In Contai
- NEET Coaching Institute In Contai
- Top Coaching Centre For NEET In Contai
- Best Coaching Centre For NEET In Contai
- Coaching Centre For NEET In Contai
- Top Coaching Institute For NEET In Contai
- Best Coaching Institute For NEET In Contai
- Coaching Institute For NEET In Contai
- Top NEET Coaching In Contai
- Best NEET Coaching In Contai
- NEET Coaching In Contai
- WBJEE Coaching In Bolpur
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Bolpur
- Top WBJEE Coaching In Bolpur
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Bolpur
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Bolpur
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Bolpur
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Bolpur
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Bolpur
- Top Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Bolpur
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In Bolpur
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In Bolpur
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In Bolpur
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In Bolpur
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In Bolpur
- Best NEET Coaching Centre In Bolpur
- NEET Coaching Centre In Bolpur
- Top NEET Coaching Institute In Bolpur
- Best NEET Coaching Institute In Bolpur
- NEET Coaching Institute In Bolpur
- Top Coaching Centre For NEET In Bolpur
- Best Coaching Centre For NEET In Bolpur
- Coaching Centre For NEET In Bolpur
- Top Coaching Institute For NEET In Bolpur
- Best Coaching Institute For NEET In Bolpur
- Coaching Institute For NEET In Bolpur
- Top NEET Coaching In Bolpur
- Best NEET Coaching In Bolpur
- NEET Coaching In Bolpur
- Top NEET Coaching Centre In Bolpur
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In BalurghatCoaching Institute For WBJEE In Balurghat
- WBJEE Coaching In Agartala
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Agartala
- Top WBJEE Coaching In Agartala
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Agartala
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Agartala
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Agartala
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Agartala
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Agartala
- Top Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Agartala
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In Agartala
- Best WBJEE Coaching Institute In Agartala
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In Agartal
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In Agartala
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In Agartala
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In Agartala
- Top NEET Coaching Centre In Balurghat
- Best NEET Coaching Centre In Balurghat
- NEET Coaching Centre In Balurghat
- Top NEET Coaching Institute In Balurghat
- Best NEET Coaching Institute In Balurghat
- NEET Coaching Institute In Balurghat
- Top Coaching Centre For NEET In Balurghat
- Best Coaching Centre For NEET In Balurghat
- Coaching Centre For NEET In Balurghat
- Top Coaching Institute For NEET In Balurghat
- Best Coaching Institute For NEET In Balurghat
- Coaching Institute For NEET In Balurghat
- Top NEET Coaching In Balurghat
- Best NEET Coaching In Balurghat
- NEET Coaching In Balurghat
- Top NEET Coaching Centre In Agartala
- Best NEET Coaching Centre In Agartala
- NEET Coaching Centre In Agartala
- Top NEET Coaching Institute In Agartala
- Best NEET Coaching Institute In Agartala
- NEET Coaching Institute In Agartala
- Top Coaching Centre For NEET In Agartala
- Best Coaching Centre For NEET In Agartala
- Coaching Centre For NEET In Agartala
- Top Coaching Institute For NEET In Agartala
- Best Coaching Institute For NEET In Agartala
- Coaching Institute For NEET In Agartala
- Top NEET Coaching In Agartala
- Best NEET Coaching In Agartala
- NEET Coaching In Agartala
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In Berhampore
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In Berhampore
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In Berhampore
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In Berhampore
- Best WBJEE Coaching Institute In Berhampore
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In Berhampore
- Top Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Berhampore
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Berhampore
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Berhampore
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Berhampore
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Berhampore
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Berhampore
- Top WBJEE Coaching In Berhampore
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Berhampore
- WBJEE Coaching In Berhampore
- WBJEE Coaching In Baruipur
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Baruipur
- Top WBJEE Coaching In Baruipur
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Baruipur
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Baruipur
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Baruipur
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Baruipur
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Baruipur ]
- Top Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Baruipur
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In Baruipur
- Best WBJEE Coaching Institute In Baruipur
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In Baruipur
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In Baruipur
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In Baruipur
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In Baruipur
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In Barrackpore
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In Barrackpore
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In Barrackpore
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In Barrackpore
- Best WBJEE Coaching Institute In Barrackpore
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In Barrackpore
- Top Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Barrackpore
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Barrackpore
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Barrackpore
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Barrackpore
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Barrackpore
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Barrackpore
- Top WBJEE Coaching In Barrackpore
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Barrackpore
- WBJEE Coaching In Barrackpore
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In Balurghat
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In Balurghat
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In Balurghat
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In Balurghat
- Best WBJEE Coaching Institute In Balurghat
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In Balurghat
- Top Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Balurghat
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Balurghat
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Balurghat
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Balurghat
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Balurghat
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Balurghat
- Top WBJEE Coaching In Balurghat
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Balurghat
- WBJEE Coaching In Balurghat
- WBJEE Coaching In Bagnan
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In Bagnan
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In Bagnan
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In Bagnan
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In Bagnan
- Best WBJEE Coaching Institute In Bagnan
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In Bagnan
- Top Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Bagnan
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Bagnan
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Bagnan
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Bagnan
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Bagnan
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Bagnan
- Top WBJEE Coaching In Bagnan
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Bagnan
- WBJEE Coaching In Arambag
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In Arambag
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In Arambag
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In Arambag
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In Arambag
- Best WBJEE Coaching Institute In Arambag
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In Arambag
- Top Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Arambag
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Arambag
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Arambag
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Arambag
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Arambag
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Arambag
- Top WBJEE Coaching In Arambag
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Arambag
- CBSE 2024 Classroom Programe
- CBSE Classroom Programme
- CBSE 2024 Classroom Programme
- CBSE 2024 Classroom Peogramme
- CBSE 2024 Mock Test
- CBSE Subjects
- CBSE 2024 Subjects
- CBSE 2024 Class
- CBSE Schedule
- CBSE 2024 Schedule
- CBSE Toppers
- CBSE 2024 Toppers
- CBSE 2024
- ICSE 2024 Classroom Programme
- ICSE Classroom Programme 2024
- ICSE Classroom Programme
- ICSE Capsule Programme 2024
- ICSE Capsule Programme
- H.S 2024 Capsule Programme
- H.S Capsule Programme
- Madhyamik Capsule Programme
- Madhyamik 2024 Capsule Programme
- mental health initiative
- mental health research
- pathfinder mental health
- mental health pathfinder
- combat mental health
- mental health literacy
- mental health awareness
- suicide cases
- suicide cases in india
- mental health issues
- mental health situation
- mental health in india
- aparajit
- this too shall pass
- thistooshallpass
- mental health
- CBSE X Board
- CBSE X 2024 Toppers
- CBSE X Toppers
- CBSE X 2024 Schedule
- CBSE X Schedule
- CBSE 2024 Class X
- CBSE X 2024 Subjects
- CBSE X Subjects
- CBSE X 2024 Mock Test
- CBSE X Mock Test
- CBSE X 2024
- CBSE X
- CBSE XII Board
- CBSE XII 2024 Toppers
- CBSE XII Toppers
- CBSE XII 2024 Schedule
- CBSE XII Schedule
- CBSE XII Class XII
- CBSE XII 2024 Subjects
- CBSE XII Subjects
- CBSE XII 2024 Mock Test
- CBSE XII Mock Test
- CBSE XII 2024
- CBSE XII
- H.S
- H.S. 2024
- H.S. Mock Test
- H.S. 2024 Mock Test
- H.S. Subjects
- H.S. 2024 Subjects
- H.S. Class XII
- H.S. Schedule
- H.S. 2024 Schedule
- H.S. Toppers
- H.S. 2024 Toppers
- H.S. Board
- Madhyamik 2024
- Madhyamik Mock Test
- Madhyamik 2024 Mock Test
- Madhyamik Subjects
- Madhyamik 2024 Subjects
- Madhyamik Class X
- Madhyamik Schedule
- Madhyamik 2024 Schedule
- Madhyamik Toppers
- Madhyamik 2024 Toppers
- Madhyamik Board
- International Junior Science Olympiad Stages
- International Junior Science Olympiad 2024 Stages
- IJSO 2024 Stages
- IJSO Stages
- IJSO 2024 Update
- IJSO Updates
- International Junior Science Olympiad 2024 Update
- International Junior Science Olympiad 2024 Updates
- International Junior Science Olympiad Exam
- International Junior Science Olympiad Syllabus
- International Junior Science Olympiad 2024 Exam Pattern
- International Junior Science Olympiad 2024 Syllabus
- IJSO Exam Pattern
- IJSO Syllabus
- IJSO 2024
- IJSO
- International Junior Science Olympiad 2024
- ICSE Board
- ISC Board
- ISC 2024 Toppers
- ISC Toppers
- ISC 2024 Schedule
- ISC Schedule
- ISC Class X
- ISC 2024 Subjects
- ISC Subjects
- ISC 2024 Mock Test
- ISC Mock Test
- ISC 2024
- ISC
- ICSE 2024 Toppers
- ICSE Toppers
- ICSE 2024 Schedule
- ICSE Schedule
- ICSE Class X
- ICSE 2024 Subjects
- ICSE Subjects
- ICSE 2024 Mock Test
- ICSE Mock Test
- ICSE 2024
- icse
- International Mathematics Olympiad 2024 Exam Date
- International Mathematics Olympiad Exam Date
- International Mathematics Olympiad 2024 Syllabus
- International Mathematics Olympiad Syllabus]
- National Science Olympiad 2024 Exam Date
- National Science Olympiad Exam Date
- National Science Olympiad 2024 Syllabus
- National Science Olympiad Syllabus
- National Science Olympiad 2024
- National Science Olympiad
- SOF NSO
- SOF NSO 2024
- International Mathematics Olympiad 2024
- International Mathematics Olympiad
- SOF IMO
- SOF IMO 2024
- International Mathematical Olympiad stages
- International Mathematical Olympiad 2024 Stages
- IMO 2024 Stages
- IMO Stages
- IMO 2024 Update
- IMO Updates
- International Mathematical Olympiad 2024 Update
- International Mathematical Olympiad 2024 Updates
- International Mathematical Olympiad Books
- International Mathematical Olympiad Syllabus
- International Mathematical Olympiad 2024 Books
- International Mathematical Olympiad 2024 Syllabus
- IMO Books
- IMO Syllabus
- IMO 2024
- IMO
- Olympiad 2024
- Olympiad
- International Mathematical Olympiad 2024
- GRADUATE PHARMACY APTITUDE TEST 2024
- GRADUATE PHARMACY APTITUDE TEST
- Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering 2024
- Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering
- CUET-UG: Common University Entrance Test 2024
- CUET-UG: Common University Entrance Test
- West Bengal Joint Entrance Examinations 2024
- West Bengal Joint Entrance Examinations
- Joint Entrance Examination 2024
- Joint Entrance Examination
- National Eligibility cum Entrance Test 2024
- National Eligibility cum Entrance Test
- GPAT 2024
- GATE 2024
- CUET 2024
- NEET UG 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024 Syllabus
- JEE Advanced 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024 Answer Key Download
- JEE Advanced 2024 Answer Key
- JEE Main 2023 Preparation
- JEE Main 2023 tips
- JEE Main 2023 Mathematics Syllabus
- JEE Main 2023 Chemistry
- JEE Main 2023 Physics Syllabus
- JEE Main 2023 Exam
- JEE Main 2023 Syllabus
- IOQM 2023 Exam Pattern
- JEE Main 2024
- IOQM Exam Pattern
- IOQM Examination 2023
- IOQM Examination
- IOQM Eligibility
- IOQM 2023 Eligibility
- IOQM Eligibility 2023
- IOQM Answer Key Download
- IOQM Answer Key 2023 Download
- IOQM 2023 Answer Key
- IOQM Answer Key
- IOQM
- IOQM 2023
- Indian Olympiad Qualifier in Mathematics (IOQM)
- JEE Main 2024 exam duration
- JEE Main 2024 important dates
- JEE Main 2024 Syllabus
- Pathfinder is always wishing the best for your JEE Advanced 2024 preparationEE Advanced 2024 Application Form is yet to be published. But
- you should know the process beforehand. Moreover
- we have talked in length about the JEE Advanced 2024 exam date and pattern which you can read right here. With that being said
- EE Advanced 2024 Application Form is yet to be published. But
- JEE Advanced 2024 important dates
- JEE Advanced 2024 registration process
- JEE Advanced 2024 FAQs
- JEE Advanced 2024 Documents
- JEE Advanced 2024 Application form correction
- JEE Advanced 2024 registration form
- JEE Advanced 2024 Application Form
- JEE Main 2024 Syllabus]
- JEE Main 2024 Counselling
- JEE Main 2024 Documents
- JEE Main 2024 Exam Mode
- JEE Main 2024 eligibility
- JEE Main 2024 registration
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Chandannagar
- Top WBJEE Coaching In Chandannagar
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Chandannagar
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Chandannagar
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Chandannagar
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Chandannagar
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Chandannagar
- Top Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Chandannagar
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In Chandannagar
- Best WBJEE Coaching Institute In Chandannagar
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In Chandannagar
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In Chandannagar
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In Chandannagar
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In Chandannagar
- WBJEE Coaching In Chandannagar
- JEE Main 2024 Exam Pattern
- JEE Main 2024 Answer Key Challenge
- JEE Main 2024 Answer Key Download
- JEE Main 2024 Exam Pettern
- JEE Main 2024 Answer Key
- JEE Advanced 2024 Academic Qualification
- JEE Advanced 2024 Foreign Students
- JEE Advanced 2024 Repeaters
- JEE Advanced 2024 Admit Card
- JEE Advanced 2024 registration fee
- JEE Advanced 2024 Eligibility
- JEE Advanced 2024 exam Date
- vso result layer 1
- vso 2023 result
- vso result 2023
- NEET 2024 Application Form
- NEET 2024 Exam Date
- NEET 2024 Counselling Date
- NEET 2024 Answer Key
- NEET 2024 Admit Card
- NEET 2024 Admit Card Date
- NEET 2024 Eligibility Criteria
- NEET 2024 Exam Syllabus
- Syllabus Of NEET 2024
- NEET 2024 Date
- wbjee admit card 2024
- Scholarship exam
- PNTSE 2023
- pathfinder national talent search examination
- scholarship exam 2023
- scholarship test 2023
- Wbjee Exam Date 2024 ]
- Wbjee 2024 Exam Date
- WBJEE 2024 Application Form
- Wbjee Exam Date 2024
- WBJEE 2024 Application Form Date
- WBJEE Application Form 2024
- WBJEE Syllabus 2024
- WBJEE 2024 Syllabus
- WBJEE 2024 Date
- Syllabus Of WBJEE 2024
- WBJEE 2024 Syllabus Pdf
- WBJEE 2024 Exam Syllabus
- WBJEE 2024 Eligibility Criteria
- WBJEE 2024 Academic Qualifications
- WBJEE 2024 Admit Card Date
- neet 2024
- wbjee 2024
- jee 2024
- pathfinder repeater course
- repeater program
- repeater programme
- repeater course
- jee main
- jee main]
- JEE
- IIT JEE
- II JEE
- wbjee
- topper 2023 neet
- neet 2023 topper lsit
- topper list 2023
- NEET 2023 toppers list
- NEET 2023 Topper List
- Neet Result
- neet merit list download link
- neet merit list download
- neet result download link
- neet result download
- neet merit list 2023
- neet result 2023
- neet scorecard 2023
- neet cutoff marks
- neet 2023 merit list
- neet ranker 2023
- ranker neet 2023
- neet 2023 ranker
- neet 2023 result
- NEET 2023 Topper List Sayan NEET Topper
- Topper of NEET 2023
- NEET Result 2023 Topper
- NEET 2023 Topper
- NEET Topper 2023
- Sayan Pradhan NEET Topper
- Cuet Application Form
- Cuet]
- 'Cuet Preparation
- Cuet Preparation]
- Cuet 2023 Examination Date]
- narayana health
- neet scholarship
- scholarship
- neet
- WBJEE Coaching In Bally
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In Bally
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In Bally
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In Bally
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In Bally
- Best WBJEE Coaching Institute In Bally
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In Bally
- Top Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Bally
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Bally
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Bally
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Bally
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Bally
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Bally
- Top WBJEE Coaching In Bally
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Bally
- VSO (Vidyasagar Science Olympiad)Answer Key 2023
- VSO 2023 Answer Key Download
- vso answer key download
- vso 2023 answer key
- vso 2023 anser key
- vso answer key
- vidyasagar science olympiad
- vso
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Tamluk
- Top WBJEE Coaching In Tamluk
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Tamluk
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Tamluk
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Tamluk
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Tamluk
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Tamluk
- Top Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Tamluk
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In Tamluk
- Best WBJEE Coaching Institute In Tamluk
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In Tamluk
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In Tamluk
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In Tamluk
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In Tamluk
- WBJEE Coaching in Tamluk.
- WBJEE Coaching In Midnapore
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In Midnapore
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In Midnapore
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In Midnapore
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In Midnapore
- Best WBJEE Coaching Institute In Midnapore
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In Midnapore
- Top Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Midnapore
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Midnapore
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Midnapore
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Midnapore
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Midnapore
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Midnapore
- Top WBJEE Coaching In Midnapore
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Midnapore
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Kalyani
- Top WBJEE Coaching In Kalyani
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Kalyani
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Kalyani
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Kalyani
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Kalyani
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Kalyani
- Top Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Kalyani
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In Kalyani
- Best WBJEE Coaching Institute In Kalyani
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In Kalyani
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In Kalyani
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In Kalyani
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In Kalyani]
- WBJEE Coaching In Kalyani
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In Cooch Behar
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In Cooch Behar
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In Cooch Behar
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In Cooch Behar
- Best WBJEE Coaching Institute In Cooch Behar
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In Cooch Behar
- Top Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Cooch Behar
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Cooch Behar
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Cooch Behar
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Cooch Behar
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Cooch Behar
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Cooch Behar
- Top WBJEE Coaching In Cooch Behar
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Cooch Behar
- WBJEE Coaching In Cooch Behar
- cuet eligibility
- cuet 2023 examination date
- cuet aplication form
- cuet examination date
- cuet admit card
- cuet syllabus
- cuet preparation
- cuet university
- cuet 2023
- cuet
- cuet 2023 preparation
- cuet 2023 syllabus
- WBJEE Coaching In Burdwan
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Burdwan
- Top WBJEE Coaching In Burdwan
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Burdwan
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Burdwan
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Burdwan
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Burdwan
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Burdwan
- Top Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Burdwan
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In Burdwan
- Best WBJEE Coaching Institute In Burdwan
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In Burdwan
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In Burdwan
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In Burdwan
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In Burdwan
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In Barasat
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In Barasat
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In Barasat
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In Barasat
- Best WBJEE Coaching Institute In Barasat
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In Barasat
- Top Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Barasat
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Barasat
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Barasat
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Barasat
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Barasat
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Barasat
- Top WBJEE Coaching In Barasat
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Barasat
- WBJEE Coaching In Barasat
- WBJEE Coaching In Bankura
- Best WBJEE Coaching In Bankura
- Top WBJEE Coaching In Bankura
- Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Bankura
- Best Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Bankura
- Top Coaching Institute For WBJEE In Bankura
- Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Bankura
- Best Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Bankura
- Top Coaching Centre For WBJEE In Bankura
- WBJEE Coaching Institute In Bankura
- Best WBJEE Coaching Institute In Bankura
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute In Bankura
- WBJEE Coaching Centre In Bankura
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre In Bankura
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre In Bankura
- Best NEET Coaching Institute Howrah
- Top NEET Coaching Institute Howrah
- NEET Coaching Institute Howrah
- Top NEET Coaching Centre Howrah
- Best NEET Coaching Centre In Howrah
- NEET Coaching Centre In Howrah
- Top NEET Coaching In Howrah
- NEET Coaching In Howrah
- Best NEET Coaching In Howrah
- Best NEET Coaching In Midnapore
- NEET Coaching In Midnapore
- Top NEET Coaching In Midnapore
- NEET Coaching Centre In Midnapore
- Best NEET Coaching Centre In Midnapore
- Top NEET Coaching Centre Midnapore
- NEET Coaching Institute Midnapore
- Top NEET Coaching Institute Midnapore
- Best NEET Coaching Institute Midnapore
- Top 5 IIT-JEE Coaching in Kolkata
- Top 10 IIT-JEE Coaching Center in Kolkata
- Top 10 IIT-JEE Coaching Centre in Kolkata
- Coaching Centre for JEE in Kolkata
- Coaching Institute for JEE
- Top 5 Coaching institute in Kolkata
- IIT-JEE Coaching in Kolkata
- JEE Coaching in Kolkata
- Best coaching for JEE in Kolkata
- Top IIT-JEE coaching institutes in Kolkata
- Top 10 JEE Coaching in Kolkata
- Best JEE Coaching in Kolkata
- Best NEET Coaching Institute Tamluk
- Top NEET Coaching Institute Tamluk
- NEET Coaching Institute Tamluk
- Top NEET Coaching Centre Tamluk
- Best NEET Coaching Centre In Tamluk
- NEET Coaching Centre In Tamluk
- Top NEET Coaching In Tamluk
- NEET Coaching In Tamluk
- Best NEET Coaching In Tamluk
- Best NEET Coaching In Baruipur
- NEET Coaching In Baruipur
- Top NEET Coaching In Baruipur
- NEET Coaching Centre In Baruipur
- Best NEET Coaching Centre In Baruipur
- Top NEET Coaching Centre Baruipur
- NEET Coaching Institute Baruipur
- Top NEET Coaching Institute Baruipur
- Best NEET Coaching Institute Baruipur
- Best NEET Coaching Institute Bally
- Top NEET Coaching Institute Bally
- NEET Coaching Institute Bally
- Top NEET Coaching Centre Bally
- Best NEET Coaching Centre In Bally
- NEET Coaching Centre In Bally
- Top NEET Coaching In Bally
- NEET Coaching In Bally
- Best NEET Coaching In Bally
- Best NEET Coaching In KTTP Township
- NEET Coaching In KTTP Township
- Top NEET Coaching In KTTP Township
- NEET Coaching Centre In KTTP Township
- Best NEET Coaching Centre In KTTP Township
- Top NEET Coaching Centre KTTP Township
- NEET Coaching Institute KTTP Township
- Top NEET Coaching Institute KTTP Township
- Best NEET Coaching Institute KTTP Township
- best institute for NEET in Kolkata
- Top NEET Coaching Institute Chandannagar
- Best NEET Coaching Institute Chandannagar
- NEET Coaching Institute Chandannagar
- Top NEET Coaching Centre Chandannagar
- Best NEET Coaching Centre in Chandannagar
- NEET Coaching Centre In Chandannagar
- Top NEET Coaching In Chandannagar
- NEET Coaching In Chandannagar
- Best NEET Coaching In Chandannagar
- Top NEET Coaching Institute In Diamond Harbour
- Best NEET Coaching Institute In Diamond Harbour
- NEET Coaching Institute In Diamond Harbour
- Top NEET Coaching Centre In Diamond Harbour
- Best NEET Coaching Centre In Diamond Harbour
- NEET Coaching Centre In Diamond Harbour
- Top NEET Coaching In Diamond Harbour
- NEET Coaching In Diamond Harbour
- Best NEET Coaching In Diamond Harbour
- Best NEET Coaching In Kharagpur
- NEET Coaching In Kharagpur
- Top NEET Coaching In Kharagpur
- NEET Coaching Centre In Kharagpur
- Best NEET Coaching Centre In Kharagpur
- Top NEET Coaching Centre In Kharagpur
- NEET Coaching Institute In Kharagpur
- Best NEET Coaching Institute In Kharagpur
- Top NEET Coaching Institute In Kharagpur
- NEET 2023 Preparation Tips
- NEET Preparation 2023
- NEET Preparation Tips
- NEET Preparation
- NEET Preparation Yips
- Top NEET Coaching Institute In Barrackpore
- Best NEET Coaching Institute In Barrackpore
- NEET Coaching Institute In Barrackpore
- Top NEET Coaching Centre In Barrackpore
- Best NEET Coaching Centre In Barrackpore
- NEET Coaching Centre In Barrackpore
- Top NEET Coaching In Barrackpore
- NEET Coaching In Barrackpore
- Best NEET Coaching In Barrackpore
- Best NEET Coaching In Barasat
- NEET Coaching In Barasat
- Top NEET Coaching In Barasat
- NEET Coaching Centre In Barasat
- Best NEET Coaching Centre In Barasat
- Top NEET Coaching Centre In Barasat
- NEET Coaching Institute In Barasat
- Best NEET Coaching Institute In Barasat
- Top NEET Coaching Institute In Barasat
- JEE Main exam
- Top NEET Coaching Institute In Arambagh
- Best NEET Coaching Institute In Arambagh
- NEET Coaching Institute In Arambagh
- Top NEET Coaching Centre In Arambagh
- Best NEET Coaching Centre In Arambagh
- NEET Coaching Centre In Arambagh
- Top NEET Coaching In Arambagh
- NEET Coaching In Arambagh
- Best NEET Coaching In Arambagh
- NEET Coaching In Arambag
- NEET Coaching In Bankura
- Best NEET Coaching In Bankura
- Top NEET Coaching In Bankura
- NEET Coaching Centre In Bankura
- Best NEET Coaching Centre In Bankura
- Top NEET Coaching Centre In Bankura
- Best NEET Coaching Institute In Bankura
- NEET Coaching Institute In Bankura
- Top NEET Coaching Institute In Bankura
- Top NEET Coaching Institute In Bagnan
- NEET Coaching In Bagnan
- Best NEET Coaching In Bagnan
- Top NEET Coaching In Bagnan
- NEET Coaching Centre In Bagnan
- Best NEET Coaching Centre In Bagnan
- Top NEET Coaching Centre In Bagnan
- NEET Coaching Institute In Bagnan
- Best NEET Coaching Institute In Bagnan
- JEE Main 2023 Exam]
- JEE Main Admit Card
- JEE Main Session 2
- JEE Main 2023 Application Form
- Engineering
- JEE Main Answer Key 2023
- JEE Main 2023
- JEE Advanced Admit Card
- JEE Advanced 2023 Exam Details
- JEE Advanced 2023
- NEET Application form date
- NEET 2023 Date
- Syllabus of NEET 2023
- NEET 2023 Exam Syllabus
- NEET 2023 Eligibility Criteria
- NEET Academic Qualification
- NEET 2023 Admit Card date
- NEET 2023 Admit Card
- NEET 2023 Answer Key
- NEET 2023 Counselling Date
- NEET 2023 Exam Date
- NEET 2023 Application form
- NEET 2023
- WBJEE 2023 Result
- WBJEE 2023 Counselling Date
- WBJEE 2023 Answer Key
- WBJEE 2023 Admit Card
- WBJEE 2023 Admit Card Date
- WBJEE 2023 Academic Qualifications
- WBJEE 2023 Eligibility Criteria
- WBJEE 2023 exam syllabus
- syllabus of WBJEE 2023
- WBJEE 2023 syllabus pdf
- WBJEE 2023 date
- WBJEE 2023 syllabus
- WBJEE application form 2023
- WBJEE syllabus 2023
- WBJEE 2023 application form
- WBJEE 2023 application form date
- wbjee exam date 2023
- wbjee 2023 exam date
- wbjee 2023
- Top NEET Coaching Institute in Burdwan
- Best NEET Coaching Institute in Burdwan
- NEET Coaching Institute in Burdwan
- Top NEET Coaching Centre in Burdwan
- Best NEET Coaching Centre in Burdwan
- NEET Coaching Centre in Burdwan
- Top NEET Coaching in Burdwan
- Best NEET Coaching in Burdwan
- NEET Coaching in Burdwan
- Top NEET Coaching Institute in Cooch Behar
- Best NEET Coaching Institute in Cooch Behar
- NEET Coaching Institute in Cooch Behar
- Top NEET Coaching Centre in Cooch Behar
- Best NEET Coaching Centre in Cooch Behar
- NEET Coaching Centre in Cooch Behar
- Top NEET Coaching in Cooch Behar
- Best NEET Coaching in Cooch Behar
- NEET Coaching in Cooch Behar
- Top NEET Coaching Institute in Berhampur
- Best NEET Coaching Institute in Berhampur
- NEET Coaching Institute in Berhampur
- Top NEET Coaching Centre in Berhampur
- Best NEET Coaching Centre in Berhampur
- NEET Coaching Centre in Berhampur
- Top NEET Coaching in Berhampur
- Best NEET Coaching in Berhampur
- NEET Coaching in Berhampur
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute in Siliguri
- Best WBJEE Coaching Institute in Siliguri
- WBJEE Coaching Institute in Siliguri
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre in Siliguri
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre in Siliguri
- WBJEE Coaching Centre in Siliguri
- Top WBJEE Coaching in Siliguri
- Best WBJEE Coaching in Siliguri
- WBJEE Coaching in Siliguri
- JEE Coaching Institute in Malda
- Best JEE Coaching Institute in Malda
- Top JEE Coaching Centre in Malda
- Best JEE Coaching Centre in Malda
- JEE Coaching Centre in Malda
- Top JEE Coaching in Malda
- Best JEE Coaching in Malda
- JEE Coaching in Malda
- Top NEET Coaching Institute in Siliguri
- Best NEET Coaching Institute in Siliguri
- NEET Coaching Institute in Siliguri
- Top NEET Coaching Centre in Siliguri
- Best NEET Coaching Centre in Siliguri
- NEET Coaching Centre in Siliguri
- Top NEET Coaching in Siliguri
- Best NEET Coaching in Siliguri
- NEET Coaching in Siliguri
- Top NEET Coaching Institute in Kalyani
- Best NEET Coaching Institute in Kalyani
- NEET Coaching Institute in Kalyani
- Top NEET Coaching Centre in Kalyani
- Best NEET Coaching Centre in Kalyani
- NEET Coaching Centre in Kalyani
- Top NEET Coaching in Kalyani
- Best NEET Coaching in Kalyani
- NEET Coaching in Kalyani
- Top NEET Coaching Centre in Durgapur
- Best NEET Coaching Centre in Durgapur
- NEET Coaching Centre in Durgapur
- Top NEET Coaching Institute in Durgapur
- Best NEET Coaching Institute in Durgapur
- NEET Coaching Institute in Durgapur
- Top NEET Coaching in Durgapur
- Best NEET Coaching in Durgapur
- NEET Coaching in Durgapur
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre in Durgapur
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre in Durgapur
- WBJEE Coaching Centre in Durgapur
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute in Durgapur
- Best WBJEE Coaching Institute in Durgapur
- WBJEE Coaching Institute in Durgapur
- Top WBJEE Coaching in Durgapur
- Best WBJEE Coaching in Durgapur
- WBJEE Coaching in Durgapur
- Top NEET Coaching Institute in Malda
- Best NEET Coaching Institute in Malda
- NEET Coaching Institute in Malda
- Top NEET Coaching Centre in Malda
- Best NEET Coaching Centre in Malda
- NEET Coaching Centre in Malda
- Top NEET Coaching in Malda
- Best NEET Coaching in Malda
- NEET Coaching in Malda
- Top NEET Coaching Institute in Kolkata
- Best NEET Coaching Institute in Kolkata
- NEET Coaching Institute in Kolkata
- Top NEET Coaching Centre in Kolkata
- Best NEET Coaching Centre in Kolkata
- NEET Coaching Centre in Kolkata
- Top NEET Coaching in Kolkata
- Best NEET Coaching in Kolkata
- NEET Coaching in Kolkata
- Top WBJEE Coaching Centre in Malda
- Best WBJEE Coaching Centre in Malda
- WBJEE Coaching Centre in Malda
- Top WBJEE Coaching Institute in Malda
- Best WBJEE Coaching Institute in Malda
- WBJEE Coaching Institute in Malda
- Top Coaching Centre for WBJEE in Malda
- Best Coaching Centre for WBJEE in Malda
- Coaching Centre for WBJEE in Malda
- Top Coaching Institute for WBJEE in Malda
- Best Coaching Institute for WBJEE in Malda
- Coaching Institute for WBJEE in Malda
- Top WBJEE Coaching in Malda
- Best WBJEE Coaching in Malda
- WBJEE Coaching in Malda
- Top 10 Coaching Centre for WBJEE in Kolkata
- Top 5 Coaching Centre for WBJEE in Kolkata
- Best Coaching Centre for WBJEE in Kolkata
- Coaching Centre for WBJEE in Kolkata
- Top 10 Coaching Institute for WBJEE in Kolkata
- Top 5 Coaching Institute for WBJEE in Kolkata
- Best Coaching Institute for WBJEE in Kolkata
- Coaching Institute for WBJEE in Kolkata
- Top 10 WBJEE Coaching Institute in Kolkata
- Top 5 WBJEE Coaching Institute in Kolkata
- Best WBJEE Coaching Institute in Kolkata
- WBJEE Coaching Institute in Kolkata
- Top 10 WBJEE Coaching in Kolkata
- Top 5 WBJEE Coaching in Kolkata
- Best WBJEE Coaching in Kolkata
- WBJEE Coaching in Kolkata
- NEET 2022 Result
- Best Coaching center for JEE Main
- Best coaching institute for JEE
- best coaching institute for boards exams in Kolkata
- best coaching institute for competitive exams in Kolkata
- Best Institute for competitive exams
- best coaching center for NEET in Kolkata
- KVPY
- KVPY 2021
- Guideline
- Strategy
- Do's & Don'ts
- JEE Advanced 2021
- Tips & Tricks
- Guida
- PNTSE 2021
- Pathfinder Scholarship Test
- Scholarship Test
- PNTSE
- CBSE
- CBSE 2021
- New Techniques
- New Pattern
- Board
- JEE Advanced
- IIT-JEE
- Book
- Class
- Lesson
- Math
- Schedule
- Study





Leave a Reply